


Next: 2.2.3 Integer
Up: 2.2 The FileData Section
Previous: 2.2.1 Overview of the
Contents
2.2.2 String
A String element declares a String parameter in the file. A String can
be any combination of letters, numbers, and special characters
(except for blank spaces, XML-reserved characters, and characters defined
as delimiters in the FileTypeSpecification root element).
Note that - at the present time - if the
target string contains a blank space, underline, or any other special
character (for example, 'Container Ship in sea state 5',
then it cannot be read as one string; it must be read as a series
of strings (one for Container, one for Ship, etc.)
or as formatted data (as A9,A1,A4,A1,A2,A1,A3,A5,A1,A1;
for more information on processing formatted data, see
Section 3.4).
The String element has no additional attributes
beyond the basics listed in Section 2.2.1.
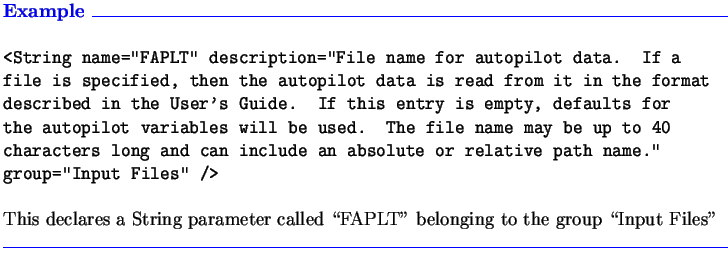
A more in-depth example is given in Section 3.1.1.



Next: 2.2.3 Integer
Up: 2.2 The FileData Section
Previous: 2.2.1 Overview of the
Contents
SAIC Ship Technology Division, Annapolis, Maryland, USA
2004-10-26

